Why Metallurgical Bonding Matters
⚙️ The Science Behind Long-Lasting Anti-Galling Coatings
🔬 What Is Metallurgical Bonding?
Metallurgical bonding is the
atomic-level fusion between the plated coating and the base metal.
Unlike mechanical adhesion, metallurgical bonding occurs when atoms from the plating layer
interdiffuse with atoms from the substrate — forming a solid, unified interface.
This bond creates a coating that is:
- Dense and non-porous
- Highly resistant to peeling, chipping, or delamination
- Able to endure extreme pressure, heat, and torque cycles
In simple terms — the coating does not just “sit” on the surface. It becomes part of it.
🧲 Why It Matters in Anti-Galling Applications
In oilfield environments, galling — the adhesion and tearing of metal surfaces under pressure — can damage threads, cause connection failure, and result in costly downtime.
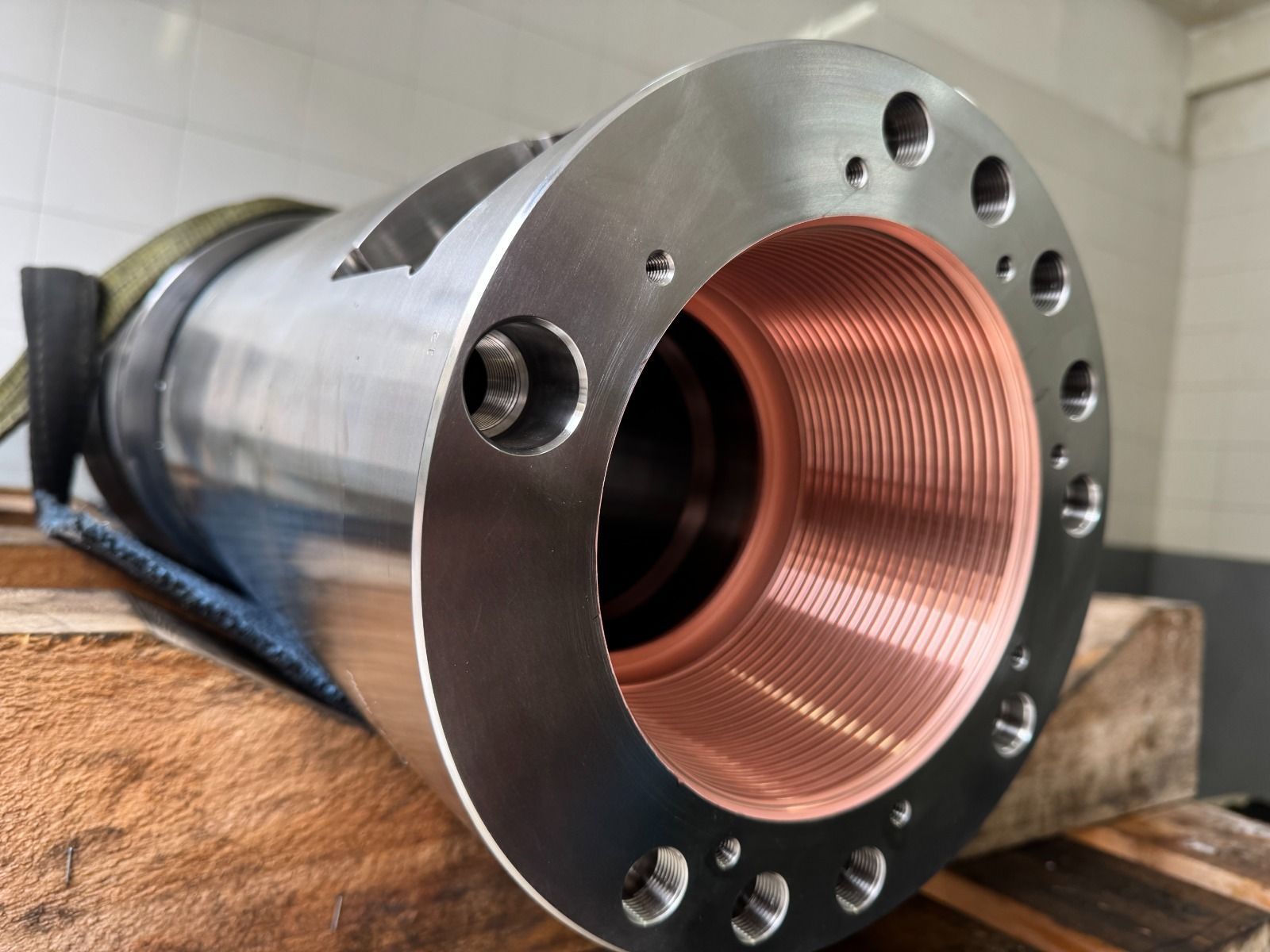
Anti-galling coatings like Copper Brush Plating provide a soft, lubricating barrier that prevents metal-to-metal contact during make-up and break-out.
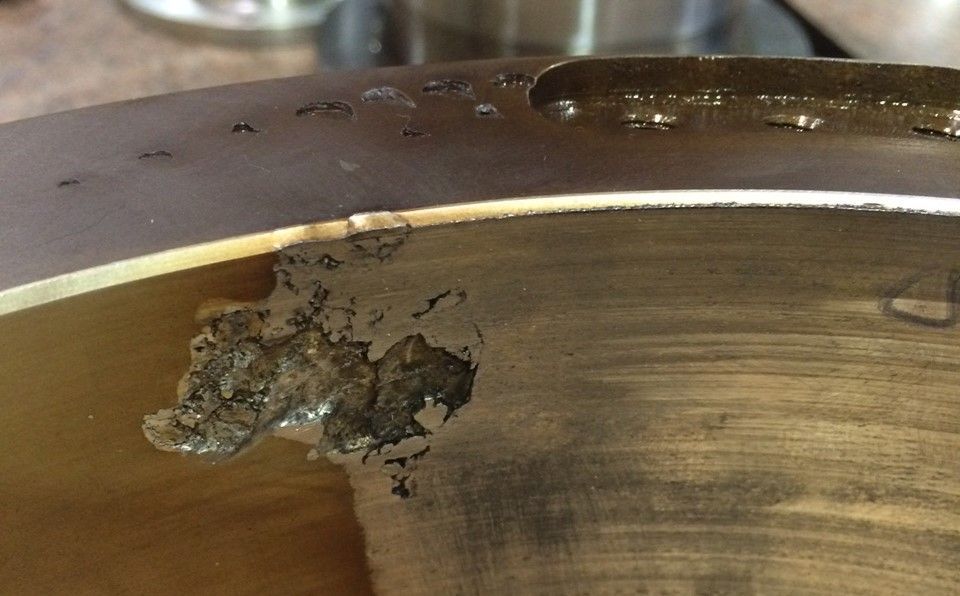
But if that coating isn’t metallurgically bonded, it can easily:
- Peel during torque application
- Crack under stress
- Transfer unevenly, leading to thread galling
This is why bond strength is the single most critical factor in ensuring coating performance and longevity.
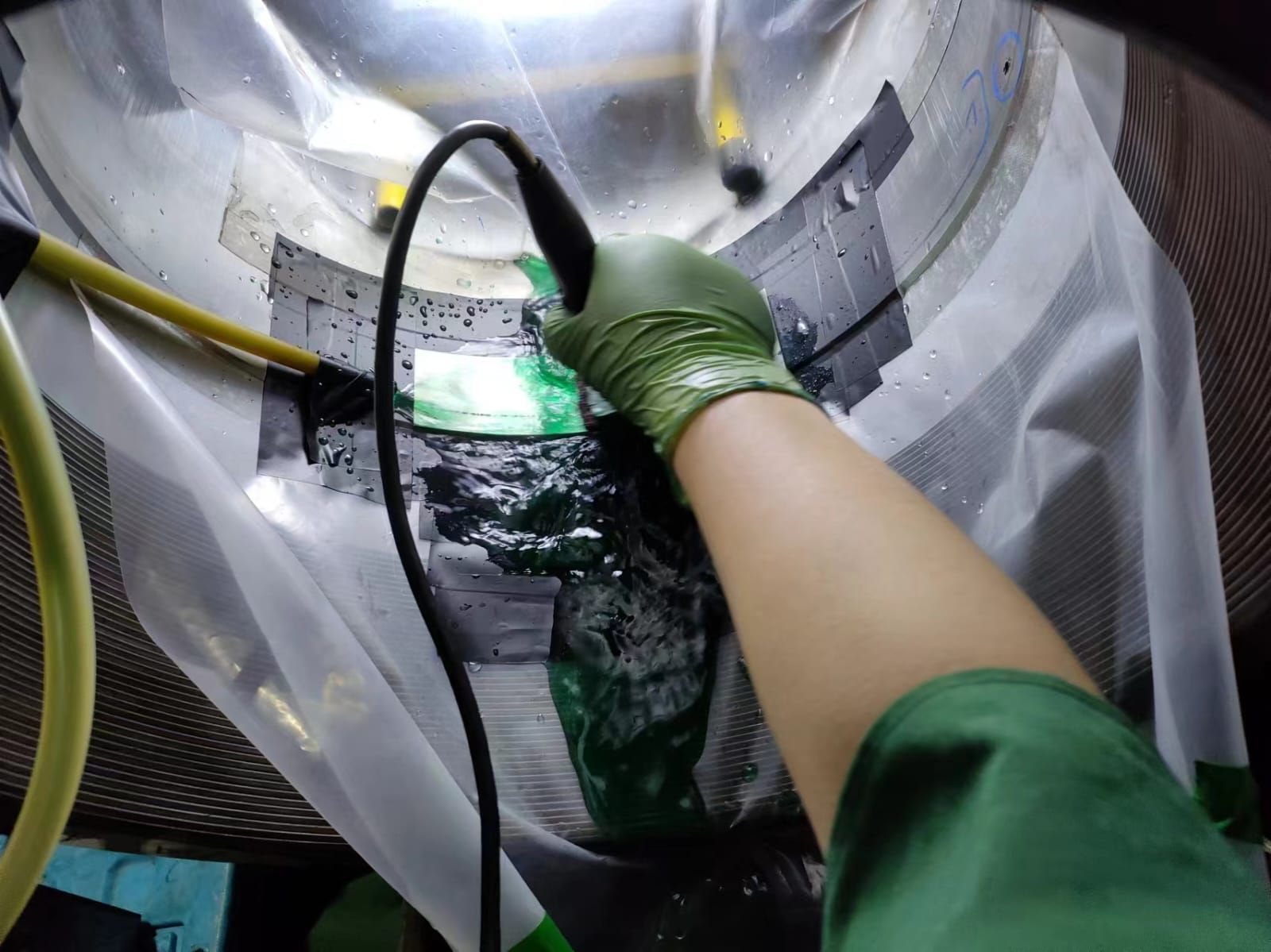
💧 The Test That Proves It — Water Jet Adhesion at 200 Bar
To verify adhesion quality, our plated coatings undergo high-pressure water jet testing — a rigorous method used in internally at Sterling Impreglon Asia.
During this test, a focused jet of water — at pressures exceeding 200 bar — is directed onto the plated surface to challenge the coating’s integrity.
Our Brush Plated coatings consistently pass without any signs of peeling, flaking, or delamination, proving the metallurgical bond’s strength and durability.
This test result is more than a quality check — it’s proof that Sterling’s process can withstand the harshest real-world conditions faced in drilling, completion, and production operations.
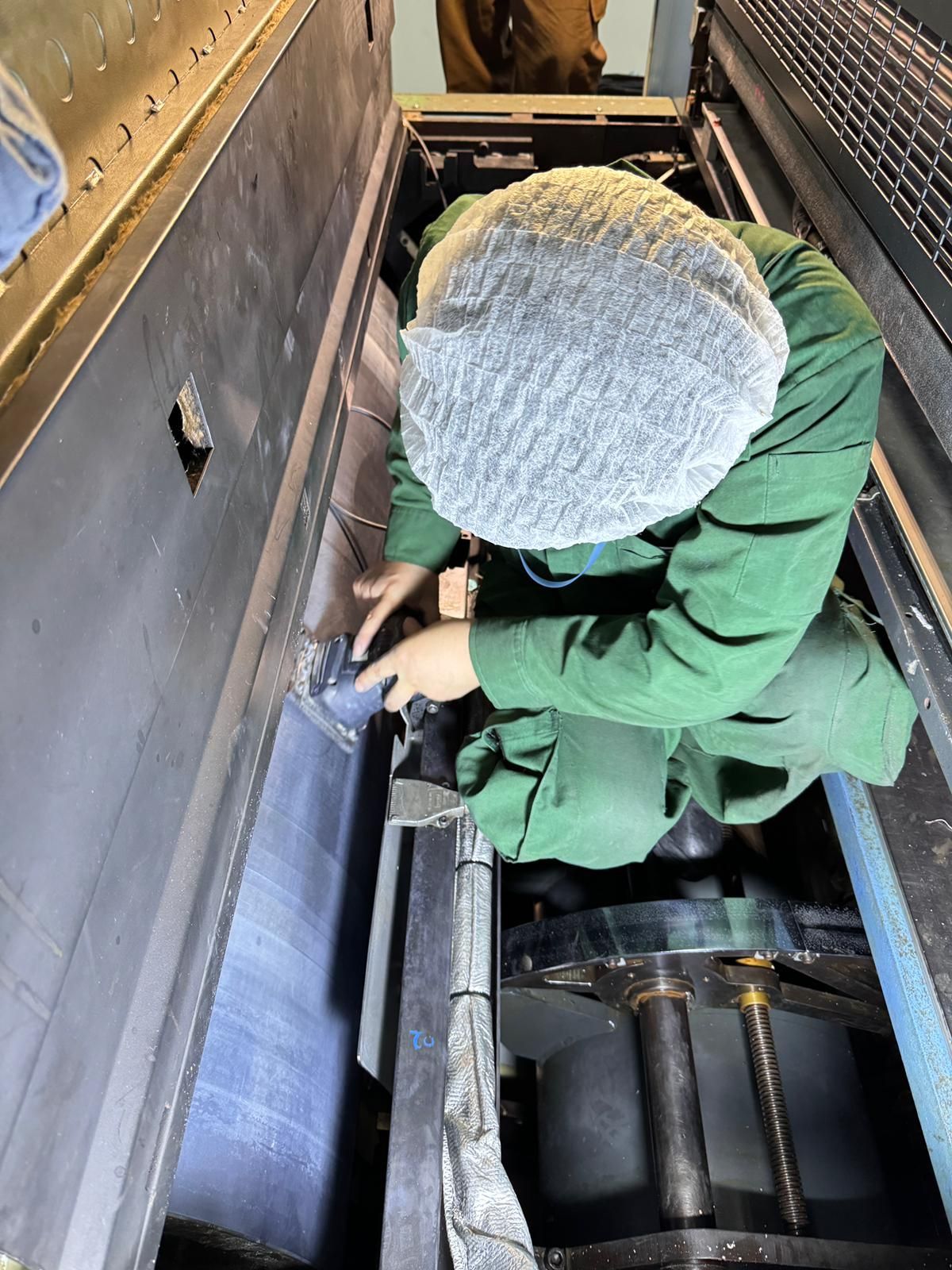
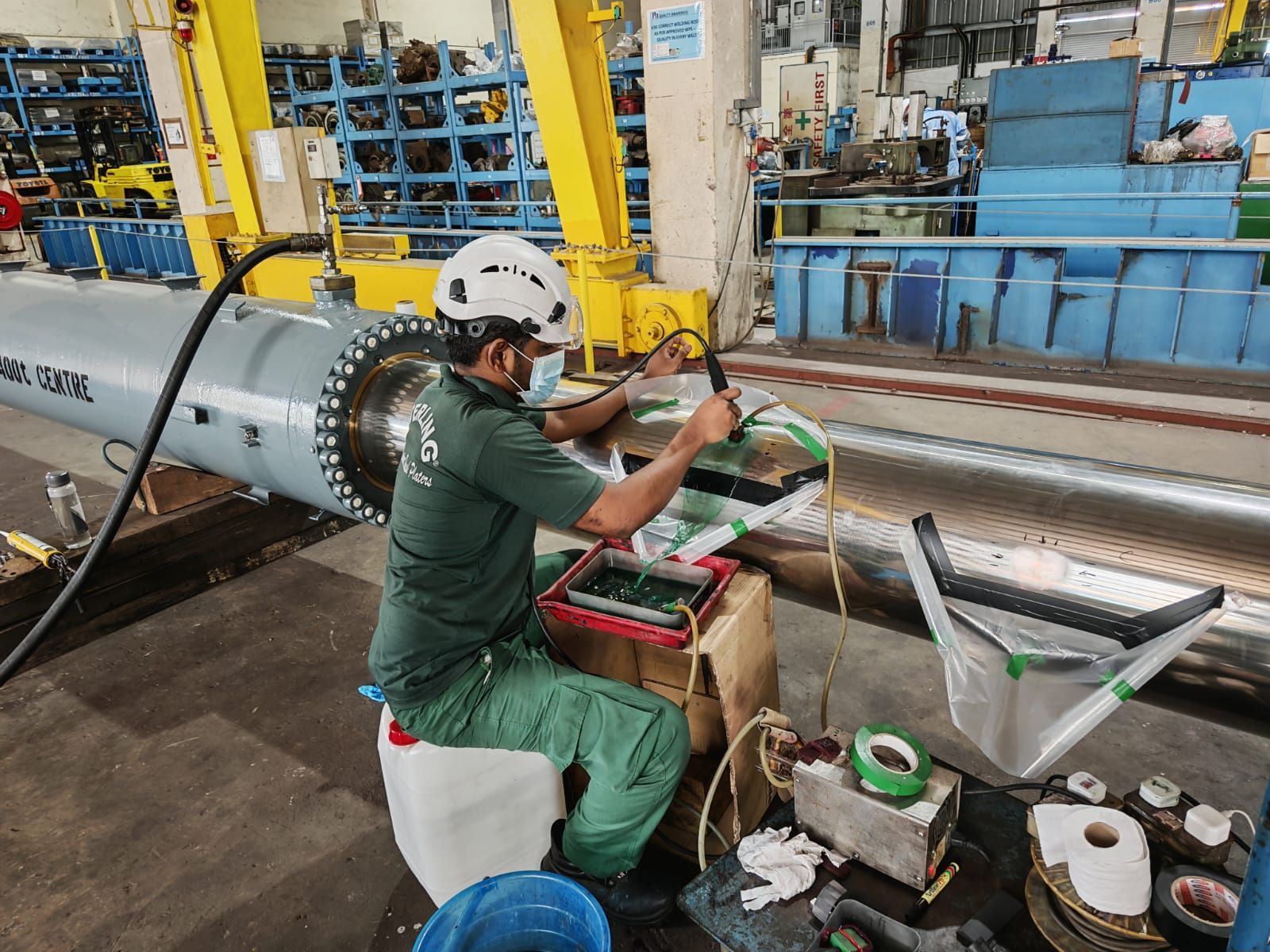
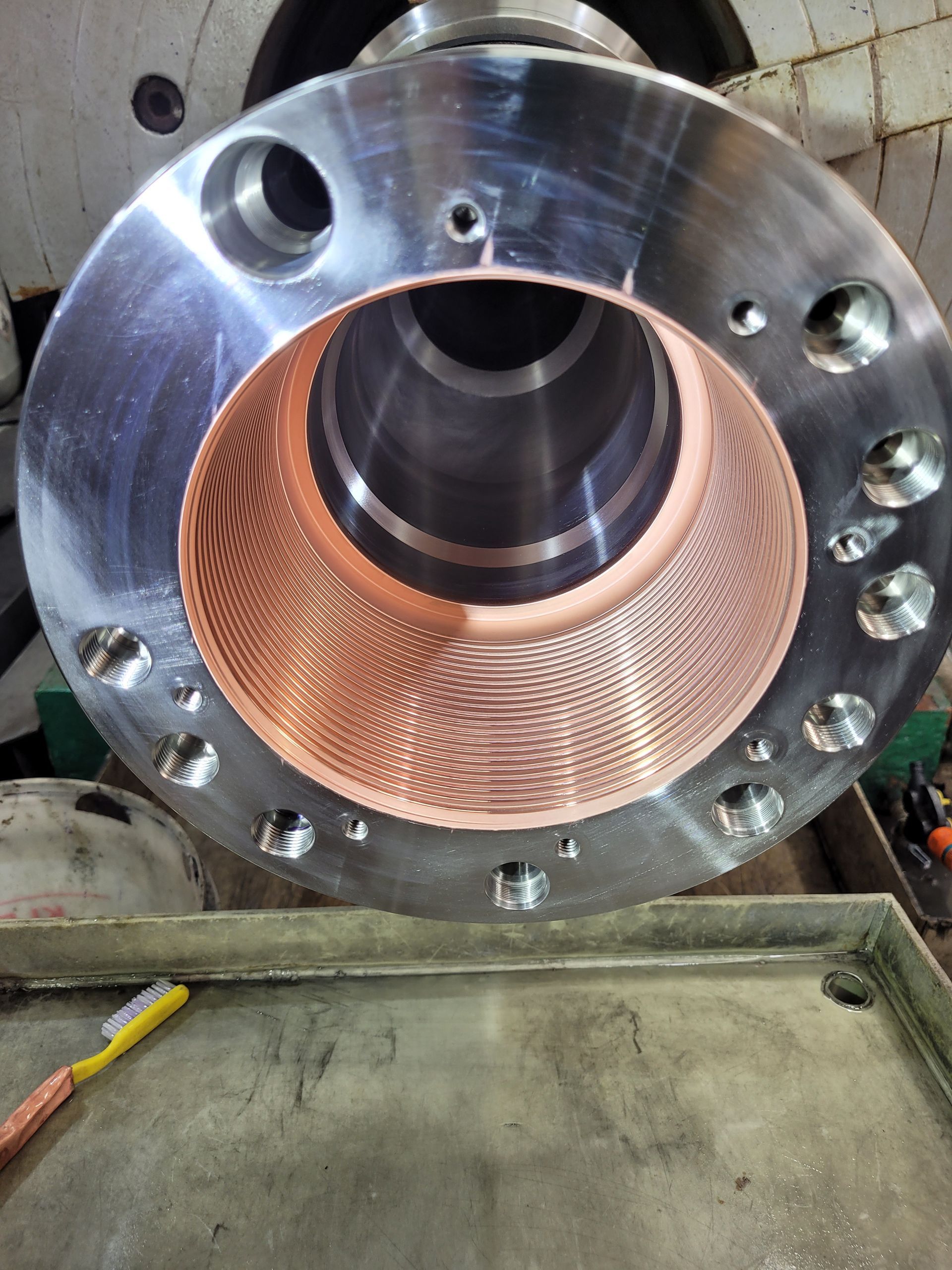
🧪 The Science Behind Sterling’s Brush Plating Process
Every successful coating begins with
surface preparation.
Our technicians meticulously clean, degrease, and activate each surface to remove oxides and contaminants — ensuring full metal-to-metal contact.
Then, using our proprietary Brush Plating setup, a metallic ion solution is applied through an anode tool under controlled voltage.
As plating occurs,
a metallurgical bond forms at the atomic level, locking the deposited layer to the base material with unmatched adhesion strength.
The result:
✅ No heat distortion or microcracks
✅ Uniform coating thickness
✅ Exceptional bonding that lasts through repeated make-up and torque cycles
🛢️ Proven and Recognized by Global Oilfield Manufacturers
Sterling Impreglon Asia’s Brush Plating process is qualified and recognized by all major OCTG and oil tool manufacturers worldwide, including VAM, Tenaris, JFE, VAGT and many more.
These industry approvals are not easily earned — they’re a testament to years of proven results, stringent testing, and consistent plating performance.
Our coatings deliver
precision, adhesion, and endurance that customers can rely on.
🌍 Metallurgical Bonding: The Unsung Hero of Reliability
When a coating fails, it’s rarely because of the plating metal itself — it’s almost always because of poor adhesion.
Metallurgical bonding ensures your coating performs as designed, even under the toughest mechanical and environmental conditions.
In a world where equipment downtime costs millions, and thread failure can halt an entire rig operation,
bond integrity is everything.
That’s why leading manufacturers continue to trust Sterling Impreglon Asia — where science, precision, and reliability meet.
📞 Trust the Experts in Metallurgical Plating Science
If your operations depend on high-performance coatings for
anti-galling, wear resistance, or corrosion protection, partner with a company that understands the science behind long-lasting adhesion.
🔗 Visit
www.sterlingimpreglonasia.com
📩 Message us or contact us for consultation and training enquiries